What Causes Dry Skin?

Dry skin or xerosis is a common dermatosis that affects people of all ages and can occur on different parts of the body. The skin needs a constant water content of 10-15% to remain intact and to maintain its flexibility. Lower hydration rates negatively affect its elasticity. What are the causes of dry skin and what can you do to alleviate the problem?
When the skin dries, itching occurs, which can later lead to cracks and even infections. These adverse effects can be minimized by using a humidifier in dry areas, changing bath products, and using lotions or moisturizers to replace lost lipid components.
What does dry skin look like?

What causes dry skin?
Xerosis or xeroderma is a common skin problem that affects millions of people around the world. It may occasionally occur due to changes in the environment, the use of a new skin care product, age, or certain diseases. Some people may suffer from chronic xerosis.
Most people experience bouts of dryness at some point during the year due to internal or external factors. Below, we present some of the causes of dry skin.
Diabetes, thyroid disease, kidney disease, contact dermatitis and atopic dermatitis can excessively dry the skin. These diseases can change both the moisture level of the skin and the eyes. In other words, they can also cause dry eyes, not just skin.
The most common symptom of dry skin is itching, a constant and sometimes unbearable side effect. This is why it is important for people with these diseases to use moisturizers continuously so that they can prevent dry skin.
Extreme weather
In the winter months when both outside and inside air is drier (think radiators), the blood moves away from the epidermis to keep the internal organs warm. This can cause the skin to dry quite quickly. In contrast, in hot and dry areas, heat from the air and the use of air conditioners remove moisture from the skin.
People living in these types of climates (and visitors) should try to take shorter showers and use hot water when possible. After that, we recommend applying moisturizer to help protect the skin.
Washing too often is one of the most common causes of dry skin. Many of the soaps and shower gels on the market contain surfactants, which break down dirt and oils on the skin. Although they cleanse the skin well, this process can dry out the skin and cause short or medium term damage.
Unfortunately, chemicals do not discriminate and remove important skin lipid barriers, allowing germs and bacteria to make their way inward.
The likelihood of xerosis increases with age, due to changes in the process of keratinization (natural exfoliation) and lipids in the outer layer of the skin.
At about 40, the body drastically decreases the production of sebum, which is responsible for keeping the skin soft and young. With each passing year, sebum production continues to decline, leading to easier drying of the skin.
Although xerosis is a common condition, it is closely linked to aging; however, there are many tips to keep your skin hydrated and healthy even at an older age.
Smoking
Cigarettes contain toxins and chemicals that can cause the skin to age prematurely. This, along with the accelerated aging process, can cause the skin to dry out even more.
People who smoke often have dry skin on their face and wrinkles around their mouths. Cigarettes accelerate the degradation of skin collagen and the small elastic fibers that form the foundation of the dermis. Because of this, cigarettes are linked to premature aging.
What is the pH of the skin and how does it relate to dry skin?
The pH scale varies from 1 to 14. The pH value of 7 is considered neutral, and anything below it is considered acidic, while anything above is alkaline. The outer layer of human skin has a pH value between 4 and 6, indicating that it is naturally acidic.
The skin has sebum, amino acids and fatty acids. All of these components are acidic, helping the skin prevent bacterial colonization. The lipid layer is also made up of fatty acids, cholesterol and ceramides that work together as a natural water repellent.
Most disease-causing bacteria are easily counteracted by the acidity of human skin. But this protective barrier cannot work effectively when the skin is dry or damaged.
The inner layers of the skin have a pH value of about 7.4, which is the ideal level for the development of bacterial colonies. Therefore, xerosis is a risk factor for infectious dermatitis.
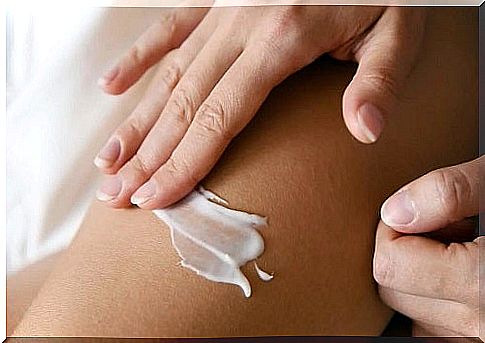
The best thing a person can do when dealing with dry skin or xerosis is to take short showers with warm water and apply a generous layer of moisturizer immediately after drying. This is when the skin is more receptive to absorbing the emollients needed to strengthen its protective barrier.
Remember that itching is a classic symptom of dry skin. So, at the first sign and even at the slightest itching, apply your favorite moisturizing lotion.









