Deep Vein Thrombosis: Detection And Prevention
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or deep phlebothrombosis occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of the deep veins of the body. In general, this problem affects the legs, but other parts of the body can also develop clots.
At the root of deep vein thrombosis may be certain blood disorders that affect clotting. Clots can also form when the patient does not move for a long time (for example, following an accident or surgery).
Deep vein thrombosis is a serious disease. Blood clots that form in the veins can circulate through the bloodstream, reaching the lungs. Once there, they can disrupt blood circulation. Some clots migrate to the heart, causing myocardial infarction.
What factors trigger deep vein thrombosis?
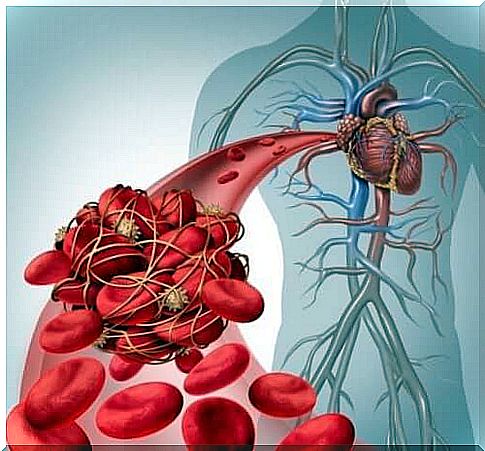
If a patient suffers from deep vein thrombosis, the blood has difficulty circulating through the veins at a great distance from the heart, ie those in the legs. As a consequence, it accumulates, leading to edema and inflammation.
Blood carried from the heart to the feet circulates through the arteries. Then it returns to the heart, after which it reaches the lungs to be oxygenated. If the blood clots in a certain vein, it cannot return to the heart. As a result, it accumulates in the legs, causing inflammation and pain. The blood clots in these parts of the body, which prevents normal blood circulation.
Blood clots associated with deep vein thrombosis can form due to any phenomenon that prevents normal blood circulation or causes excessive clotting. For example, they may occur after surgery or as a side effect of certain medications and limited movement.
There are certain risk factors that increase the susceptibility to deep vein thrombosis. These include:
- Genetic inheritance: Some people inherit diseases that trigger circulatory problems.
- Lack of movement: For example, due to hospitalization.
- Injuries and surgeries
- Pregnancy, overweight or obesity
- Smoking
How is deep vein thrombosis detected?
First of all, we must mention that many diseases cause signs and symptoms similar to those of deep vein thrombosis. This category includes pulmonary embolisms, muscle injuries, cellulite and inflammation of superficial veins. Therefore, the patient must undergo investigations so that the doctor can locate the clot and make a correct diagnosis.
Here are the main methods to use:
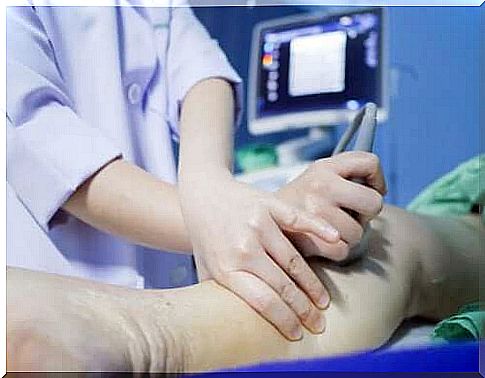
Duplex ultrasound
This method involves using sound waves to generate images of blood flow through the veins. Duplex ultrasound can detect blockages or blood clots in the deeper veins. It is the standard imaging method for diagnosing deep vein thrombosis.
Determination of D-dimers
This test measures the level of a substance released into the blood when a clot degrades. A negative result suggests that the patient is unlikely to suffer from deep vein thrombosis and vice versa.
Phlebography
Phlebography is the most accurate method of diagnosing blood clots. Unfortunately, it is an invasive procedure, as the doctor has to use tools to manipulate the patient’s body.
Phlebography is a special radiograph that involves inserting a special contrast substance into one of the large veins of the foot or ankle. Thus, the deep veins of this limb can be seen.
MRIs and CTs
These two methods help doctors diagnose and treat many diseases. The images show the veins and any clots present. CT and MRI are not frequently used in the diagnosis of deep phlebothrombosis, but, if necessary, are accessible diagnostic methods.
Prevention of deep vein thrombosis

Preventing deep vein thrombosis is to improve blood flow to the heart. It is very important for the patient to consult a doctor, in order to be recommended an exercise routine.
It is also advisable to keep your legs raised to facilitate blood circulation. The most comfortable way to do this is to lift the part of the mattress on which the legs rest, so that they are slightly raised.
If you are a smoker, we advise you to give up this habit. Tobacco is a risk factor for many heart problems. Doctors recommend that we exercise for 30 minutes, at least three times a week. At the same time, it is advisable to eat more foods that prevent blood clots.
If needed, your doctor may prescribe anticoagulant medications to prevent this type of problem.